In global logistics, visibility is everything—but when it comes to air cargo tracking, compliance can make or break a shipment. Understanding air cargo tracker approvals is essential for freight forwarders, shippers, and logistics managers, especially in industries where cargo integrity isn’t negotiable.
This guide breaks down the current approval landscape, what regulators and airlines require, and how GEGO supports compliant, scalable tracking for critical supply chains.
Why Air Cargo Tracker Approvals Matter
Safety, Compliance, and Avoiding Shipment Delays
Tracking devices introduce electronics—and often lithium batteries—into tightly regulated aircraft cargo holds. That’s why regulators and airlines have developed strict rules to ensure that devices used in transit are safe, non-interfering, and documented.
If a tracker doesn’t meet those standards, your cargo could face delays, denial of carriage, fines, or in some cases, regulatory scrutiny.
Risks of Non-Approved Devices
- Blocked shipments or offloading at origin
- Carrier penalties for undeclared electronic items
- Compliance investigations (especially in pharma, biotech, and cold chain sectors)
- Loss of credibility with partners and customers
Who Governs Tracker Approvals?
FAA, EASA, IATA Guidance
Global regulation starts with the major aviation authorities:
- FAA (U.S.) and EASA (Europe) define safety standards for devices with lithium batteries, electromagnetic emissions, and in-flight use.
- IATA provides detailed guidelines on the transport of electronic devices and smart cargo tracking systems, including best practices for lithium battery declaration and packaging.
These bodies don’t “approve” specific devices—but they set the rules manufacturers and shippers must follow.
Airline-Specific Approval Processes
Beyond regulations, each airline has its own approval criteria. Some carriers require documentation for:
- Lithium battery type (e.g., lithium-ion vs lithium metal)
- RF (radio frequency) transmission specs
- Operating modes (e.g., flight mode or transmission shutoff during flight)
Others may need formal acceptance testing, prior notice, or integration into their own cargo systems.
Common Approval Requirements
Battery Type and Lithium Restrictions
Lithium batteries are strictly regulated under IATA DGR (Dangerous Goods Regulations). Most airlines allow devices with:
- < 2.7 Wh lithium-ion batteries
- < 0.3 g lithium metal content
Trackers must also disable transmission during flight or prove low risk in continuous mode.
RF Emissions and Network Compatibility
To prevent interference with aircraft systems, devices must emit RF signals within safe thresholds, typically defined by the airline. Most demand documentation proving low-power transmission, automatic shutoff, or compliance with flight-safe operating modes.
Certification and Documentation
Trackers often need:
- Technical specification sheets
- Lithium battery test summaries (UN 38.3)
- Safety data sheets (SDS)
- Compliance letters or airline approval letters (where applicable)
Current Approvals Landscape (2025)
Regional Differences
Regulatory enforcement varies by region. U.S.-based airlines closely follow FAA and TSA guidelines, while EU carriers may enforce EASA and local aviation authority rules. Asian and Middle Eastern carriers have unique processes, often requiring manual pre-clearance.
Airline-by-Airline Variation
There is no universal tracker whitelist. One airline may accept a GPS+Bluetooth tracker with continuous transmission; another might block it outright unless in flight mode.
That’s why scalable solutions like GEGO are designed to meet baseline regulatory standards while being adaptable across airlines.
Impact on Global Shippers
With so much variation, shippers moving high-value or sensitive goods globally must:
- Vet tracker devices before deployment
- Maintain compliance documentation for all shipments
- Partner with logistics providers that understand tracker compliance
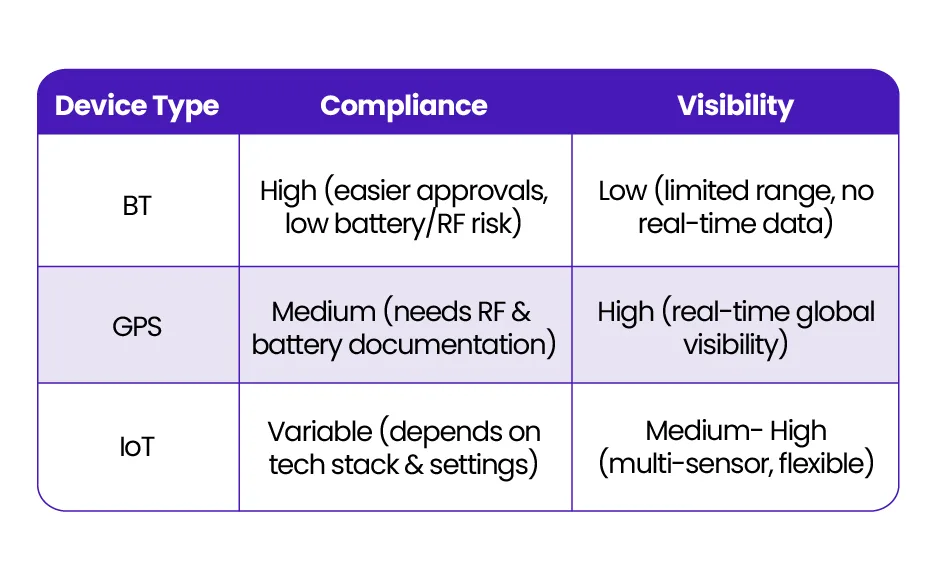
Device Types & Compliance Complexity
Bluetooth-Only Trackers
Pros: Low battery risk, limited RF emissions
Cons: Limited range, no real-time visibility in cargo
These often meet airline approval more easily—but provide minimal data for critical cargo.
GPS/Cellular Trackers
Pros: Real-time global visibility
Cons: Higher power output, require RF documentation
These offer the best supply chain intelligence—but need careful configuration and documentation.
Emerging IoT Trackers
Pros: Multi-sensor (temp, shock, humidity), network-flexible
Cons: Compliance depends on tech stack and settings
Powerful but complex, these require close coordination with airlines and logistics partners.
GEGO’s Approach to Compliance
Airline-Friendly Design
GEGO trackers are engineered for air cargo compatibility:
- Small lithium batteries within safe thresholds
- RF emissions compliant with airline standards
- Flight-safe operating modes
While we don’t claim universal airline “approvals,” our design philosophy aligns with aviation requirements and compliance best practices.
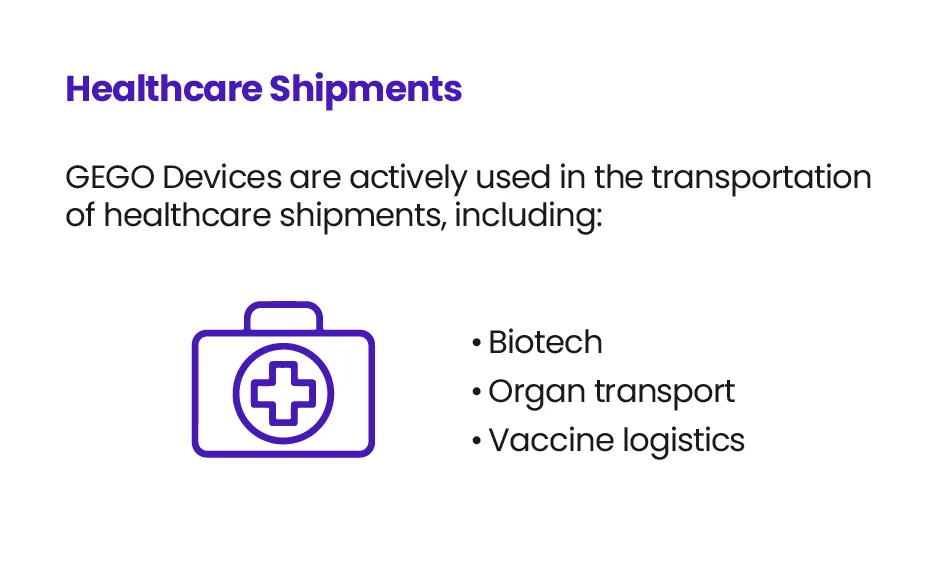
Healthcare & Life Sciences Proof Points
GEGO devices are actively used in biotech, organ transport, vaccine logistics, and other sensitive healthcare shipments—industries with zero margin for error.
Our customers include freight forwarders and 3PLs serving:
- Organ procurement organizations (OPOs)
- Biologics manufacturers
- Cold chain pharma logistics
Partner Enablement & Scalability
We provide:
- Technical documentation for airlines
- Guidance for freight forwarders and shippers
- Flexible API integrations and device configurations for B2B partners
GEGO enables end-to-end monitoring without risking regulatory violations.
Conclusion — Navigating Airline Approvals with Confidence
In 2025, air cargo tracker approvals are a moving target. But non-compliance isn’t an option—especially for pharma, biotech, and high-value logistics. By understanding global rules, preparing the right documentation, and using compliant technology like GEGO, shippers can unlock full shipment visibility without the regulatory risk.
Request a consultation on GEGO’s airline-compliant solutions
FAQ
What is an air cargo tracker approval?
It’s the process of ensuring a tracking device meets airline and aviation authority requirements for safe use in air cargo.
Who regulates cargo tracking devices?
FAA (U.S.), EASA (EU), IATA, and individual airlines.
Do all airlines follow the same approval standards?
No—each airline can set its own rules based on battery type, RF output, and documentation.
What are common requirements for approval?
Safe battery specs, RF emissions compliance, and full technical documentation.
How can shippers stay compliant?
Use approved devices, maintain documentation, and partner with providers like GEGO that understand airline standards.